Remote Code Execution is a security flaw that allows an attacker to run arbitrary code or system commands on a target server without authorization. This typically occurs when user input is passed to interpreters, command execution functions, or unsafe file handling mechanisms without proper validation. Because it leads directly to system compromise, RCE is classified as a critical vulnerability.
This blog explains what RCE is, why it is so impactful, and how it can be detected and mitigated using structured security testing approaches.
RCE vulnerabilities are frequently exploited in real-world breaches to deploy malware, exfiltrate data, and pivot into internal networks. Attackers often chain RCE with phishing, file uploads, or vulnerable libraries to achieve persistent access and lateral movement across environments. These attacks highlight why early detection and prevention of RCE is essential for protecting business operations.
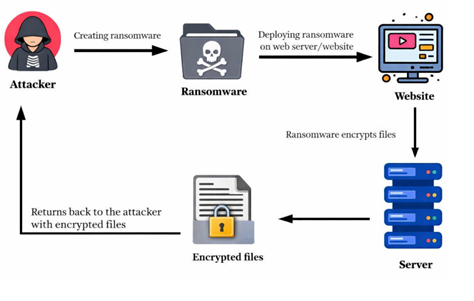
Traditionally, identifying RCE vulnerabilities required manual code review, penetration testing, and exploitation validation by highly skilled analysts. This process is slow, labour-intensive, and difficult to scale across large application portfolios. As application complexity grows, manual testing alone becomes insufficient to keep up with emerging threats.
Modern security testing combines automated scanning, dynamic testing, and manual validation to identify RCE risks quickly and accurately. This layered approach enables organizations to:
Under the Hood: How SSL Pinning Bypass Is Identified
Step 1: Network behavior analysis
Route application traffic through an intercepting proxy to observe whether SSL pinning blocks HTTPS interception.
Step 2: Static analysis
Analyze the application package (APK/IPA) to identify SSL/TLS implementation components such as
TrustManager, HostnameVerifier, or certificate pinning libraries.
Step 3: Runtime instrumentation
Apply controlled runtime testing using instrumentation frameworks to disable certificate validation logic
dynamically.
Step 4: Traffic validation
Confirm vulnerability by verifying whether decrypted HTTPS traffic becomes visible in the proxy after bypassing
pinning.
Step 5: Reporting and remediation
Document the findings, assess the impact on data confidentiality and integrity, and provide secure implementation
guidance
for enforcing strong SSL pinning controls.
RCE detection integrates into secure development and operational workflows through: